Although LEDs (lights) have been used in the world since the 60s, the question of how to connect them correctly is still relevant today.
Let's start with the fact that all LEDs operate exclusively from direct current. For them, the polarity of the connection, or the location of the plus and minus, is important. If the connection is incorrect. the LED will not work.
How to determine LED polarity
LED polarity can be determined in three ways:

N.B. Although in practice the latter method is sometimes not confirmed.
Be that as it may, it should be noted that if you briefly (1-2 seconds) do not connect the LED correctly, then nothing will burn out and nothing bad will happen. Since the diode itself works in one direction, but not in the opposite direction. It can burn out only due to increased voltage.
The nominal voltage for most LEDs is 2.2 - 3 volts. LED strips and modules that operate at 12 volts or more already contain resistors in the circuit.
How to connect an LED to 12 volts
Connecting the LED directly to 12 volts is prohibited; it will burn out in a split second. A limiting resistor (resistance) must be used. The resistor size is calculated using the formula:
R= (Upit-Upad)/0.75I,
where R is the resistance value of the resistor;
Upit and Upad – supply voltage and falling voltage;
I – passing current.
0.75 — reliability coefficient for the LED (constant value)
For greater clarity, let's look at the example of connecting one LED to a 12 volt car battery.
In this case:
- Upit - 12 volts (car battery voltage)
- Updrop - 2.2 volts (LED supply voltage)
- I - 10 mA or 0.01 A (current of one LED)
Using the above formula, we get R=(12-2.2)/0.75*0.01 = 1306 Ohm or 1.306 kOhm
The closest standard resistor value is 1.3 kiloohms
That's not all. It is necessary to calculate the required minimum resistor power.
But first, let's determine the actual current I (it may differ from that indicated above)
Formula: I = U / (Rres. + Rlight)
- Rlight - LED resistance:
Upd.nom. / Inom. = 2.2 / 0.01 = 220 Ohm,
It follows from this that the current in the circuit
I = 12 / (1300 + 220) = 0.007 A
The actual LED voltage drop will be:
And finally, the power is:
P = (Up. - Up.)² / R = (12 -1.54)²/ 1300 = 0.0841 W).
You should take a little more power than the standard size. In this case, 0.125 W is better.
So, in order to correctly connect one LED to 12 volts (car battery), you will need to insert a resistor into the circuit with a resistance 1.3 kOhm and power 0.125 W.
The resistor can be connected to any leg of the LED.
For those who got a bad grade in math at school, there is a simpler option. When purchasing LEDs at a radio store, ask the seller which resistor you will need to insert into the circuit. Don't forget to indicate the voltage in the circuit.
How to connect an LED to 220V
The dimension of resistance in this case is calculated in a similar way.
The initial data is the same. LED consumption 10 mA and voltage 2.2 volts.
Only the supply voltage is 220 volts AC.
R = (Upit.-Up.) / (I * 0.75)
R = (220 - 2.2) / (0.01 * 0.75) = 29040 Ohm or 29,040 kOhm
The closest nominal resistor is a standard value of 30 kOhm.
Power is calculated using the same formula.
First, we determine the actual current consumption:
I = U / (Rres.+ Rlight)
Rlight = Upnom. / Inom. = 2.2 / 0.01 = 220 Ohm,
and from this it follows that the current in the circuit will be:
I = 220 / (30000 + 220) = 0.007 A
Thus the real LED voltage drop will be:
Upd.light = Rlight * I = 220 * 0.007 = 1.54 V
And finally the resistor power:
P = (Up. - Up.)² / R = (220 -1.54)² / 30000 = 1.59 W)
The resistance power should be at least 1.59 W, preferably a little more. The nearest higher standard value is 2 W.
So, to connect one LED to a voltage of 220 volts, we need to place a resistor with a nominal value of 30 kOhm and power 2 W.

BUT! Since in this case the current is alternating, the LED will light only in one half-phase, that is, it will blink very quickly, at approximately 25 flashes per second. The human eye does not perceive this and it will seem that the light is usually on. But in fact, it will still miss reverse breakouts, although it only works in one direction. To do this, you need to put a reverse directional diode in the circuit in order to balance the network and protect the LED from premature failure.
- Incorrect installation and connection with errors
Here are the main three rules and mistakes that you need to pay attention to first.
1 rule

The LED strip is connected in parallel, in sections of no more than 5 meters each.
It is even sold in reels of this meter. What if you need to connect 10 or 15m? It would seem that you connect the end of the first piece with the beginning of the second and you're done. However, such connection is prohibited. Why is this so accepted?
Because five meters is effective length, which the current-carrying tracks of the tape can withstand. With a longer length, the load will exceed the permissible one and the tape will definitely fail. In addition, uneven glow will be observed. At the beginning of the strip, the LEDs will shine brightly, and at the end they will be much dimmer.
This is what a parallel connection diagram for LED strips with a length exceeding the permissible length will look like: 
In this case, the tape can be connected both from two sides and from one. Connecting on both sides allows you to reduce the load on the current paths, and also helps to avoid uneven glow at the beginning and end of the tape. 
This is especially important on a powerful tape - over 9.6 W/meter. This is exactly how professionals who have been installing LED products for many years advise connecting. The only big drawback is that you have to drag additional wires along the entire lighting.
Rule 2

The LED strip must be mounted on an aluminum profile, which acts as a heat sink.
During operation, the tape heats up, and this temperature negatively affects the LEDs themselves. They simply overheat and begin to lose brightness, gradually degrading and collapsing.
Thus, a tape that could easily work for 5-10 years without a profile will burn out in a year, and maybe even earlier. Therefore, the use of aluminum profiles in LED backlight Necessarily. 
The only tape where you can do without it is SMD 3528. It is low-power, only 4.8 W per 1 m and is not so demanding on heat dissipation. 
Tapes filled with silicone on top especially need heat removal. In them, heat transfer occurs only through the substrate, from below. And sometimes this is not enough. If you also stick it on some plastic or wood, then there will be no cooling at all.
Rule 3
 The correct choice of power supply is a guarantee of long-term and safe operation of the entire backlight.
The correct choice of power supply is a guarantee of long-term and safe operation of the entire backlight.
The power supply must be more powerful than LED Strip Light by 30%.
Only in this case will it work normally. If you select it closely, exactly according to the power of all LEDs, then the unit will constantly work at its limit. Naturally, such work will affect the duration of operation. So always give him some extra.
Connecting LED strip
To install lighting using LED strip you will need:





Installation of 220V power supply
If you have not completed electrical installation work, then you must first supply 220V voltage to the connection point of the tape. To do this, ditch the wall, or lay a cable channel and stretch a three-core VVGng-Ls 3*1.5 cable along it. Lead it directly to the distribution box where the power supply for the LED strip will be connected. 
You can use the existing junction box where the main lighting is connected. The main thing is that the space allows you to freely connect additional wires and terminal blocks.
It is advisable to install the switch on the LED strip on the 220 Volt wires, and not in front of the strip on the outgoing 12-24V. In this case, the unit will not work continuously. Especially, pulse blocks working without load is contraindicated. In addition, this will increase the level of security. 
Pre-check and do not confuse phase, neutral and ground. Most often, zero happens of blue color, the grounding conductor is yellow-green, and the phase conductor is of any other colors.
But you can’t trust color coding alone! More details on how to distinguish zero and phase without errors can be found in the article “How to determine phase and zero in electrical wiring.” 
Next, you need to lay a cable from this junction box in a groove, corrugated sleeve or in a cable channel to the future location of the power supply. To place it, install a convenient shelf. It can be made from pieces of plywood or drywall. Place a dimmer nearby. 
Connecting the power supply
Having stretched the cable to the block, you can proceed directly to connecting the wires.
- connect the phase wire to connector L
- blue wire - zero, to terminal N
- yellow-green - to the terminal marked as Pe or with a ground symbol
Dimmer connection
Now you need to connect the dimmer. Use flexible here installation wire PuGV 1.5mm2 in different colors. For example, black (for negative contacts) and red (for positive ones).
- measure and cut the required wire size
- clean the ends and crimp them with NShVI tips
 First of all, connect the ends from the power supply side. Connect the negative wire (black) to the terminal marked –V. Positive wire (red) with terminal marked as +V.
First of all, connect the ends from the power supply side. Connect the negative wire (black) to the terminal marked –V. Positive wire (red) with terminal marked as +V.
Both wires must be connected to the dimmer side Power IN(input power). Connect the red wire on the dimmer to the positive terminal DC+, and the other wire to the minus terminal DC-
Next comes the installation work of laying the wire again. Stretch it in a corrugation from the dimmer to the point of connection to the LED strip. Use the same PuGV. If the total length of the LED strip and backlight exceeds 5 meters, the strips are connected in parallel. Moreover, each of them is supplied with separate power. 
Proceed to connect the wires to the dimmer terminals. They usually have an inscription and are designated as Output Led. For reliable contact, it is better to crimp the stripped ends of the cores with tips. 
Installation and soldering of wires on LED strip
You can proceed to installing the tape itself. To do this, you need to measure it and cut it into the required pieces. This can not be done in any place, but only where the dotted line is applied or scissors are drawn. 
After cutting, the wires can be soldered to special contacts on the tape. For the same purposes, as well as for connecting individual pieces of tape to each other, connectors can be used. 
Look for the negative terminal and connect black wires there. Accordingly, another wire goes to the plus contact - red. Do not heat the soldering iron to maximum, otherwise you will easily burn the substrate. Recommended soldering time is up to 10 seconds. 
The opposite ends are also cleaned and NShVI tips are installed on them. 
Remember once again that for better cooling, you only need to lay the LED strip on an aluminum profile. It is installed in advance.
After all this work, all wire strands are brought out to one place and connected to the corresponding supply wires, observing the phasing (positive and negative contacts). 
The connection is best made using Wago terminals.
The most correct connection of several LEDs is in series. Now I will explain why.
The fact is that the determining parameter of any LED is its operating current. It is the current through the LED that determines what the power (and therefore the brightness) of the LED will be. It is the excess of the maximum current that leads to an excessive increase in the temperature of the crystal and failure of the LED - rapid burnout or gradual irreversible destruction (degradation).
Current is the main thing. It is indicated in the technical characteristics of the LED (datasheet). And depending on the current, the LED will have one voltage or another. Voltage can also be found in the reference data, but it is usually indicated in the form of a certain range, because it is secondary.
Serial connection
When LEDs are connected in series, the same current flows through them. The number of LEDs does not matter, it could be just one LED, or it could be 20 or even 100 pieces.
For example, we can take one 2835 LED and connect it to a 180mA driver and the LED will operate normally, delivering its maximum power. Or we can take a garland of 10 of the same LEDs, and then each LED will also work in normal passport mode (but the total power of the lamp, of course, will be 10 times greater).
Below are two LED switching circuits, pay attention to the difference in voltage at the driver output: 
So to the question of how the LEDs should be connected, serial or parallel, there can only be one correct answer - of course, serial!
The number of LEDs connected in series is limited only by the capabilities of the driver itself.
Ideal driver can endlessly increase the voltage at its output to ensure required current through the load, so an infinite number of LEDs can be connected to it. Well, real devices, unfortunately, have a voltage limit not only from above, but also from below.
Here is an example of a finished device: 
We see that the driver is able to regulate output voltage only within 64...106 volts. If to maintain a given current (350 mA) you need to raise the voltage above 106 volts, then it’s a bummer. The driver will output its maximum (106V), and what the current will be is no longer dependent on it.
And, conversely, you cannot connect too few LEDs to such an LED driver. For example, if you connect a chain of 10 LEDs connected in series to it, the driver will not be able to lower its output voltage to the required 32-36V. And all ten LEDs will most likely just burn out.
The presence of a minimum voltage is explained (depending on the circuit design) by limitations on the power of the output control element or by exceeding the limiting generation modes of the pulse converter.
Of course, drivers can be for any input voltage, not necessarily 220 volts. Here, for example, is a driver that converts any source permanent voltage (power supply) from 6 to 20 volts into a 3 A current source: 
That's all. Now you know how to turn on an LED (one or more) - either through a current-limiting resistor or through a current-setting driver.
How to choose the right driver?
Everything is very simple here. You only need to choose according to three parameters:
- output current;
- maximum output voltage;
- minimum output voltage.
Output (operating) current of the LED driver- this is the most important characteristic. The current should be equal to the optimal current for LEDs.
For example, we had 10 full-spectrum LEDs at our disposal for: 
The rated current of these diodes is 700 mA (taken from the reference book). Therefore, we need a 700 mA current driver. Well, or a little less to extend the life of the LEDs.
Driver maximum output voltage must be greater than the total forward voltage of all LEDs. For our phytoLEDs, the forward voltage is in the range of 3...4 volts. We take it to the maximum: 4V x 10 = 40V. Our driver must be able to output at least 40 volts.
I receive a lot of questions from readers about how to properly connect LEDs to 12 volts and to a 220V network. Usually they only know that the LED connection circuit can be parallel or serial. But diodes are not only single-color, but also three-color RGB and four-color RGBW. To control them, an RGB controller is required.

- 1. How to connect LED
- 2. LED designation on the diagram
- 3. Characteristics
- 4. Assembly steps
- 5. Power supplies
- 6. Connection to a 1.5V battery
- 7. Powered by 5V
- 8. Switch on 9V
- 9. How to connect an LED to 12 volts
- 10. How to connect an LED to 220V
- 11. Connection to 220V without a driver
- 12. RGB LEDs and color
How to connect an LED

Basic specifications LEDs are described by three parameters:
- direct voltage;
- rated operating current;
- rated power.
The most common LED chips have direct voltages in the region of 3, 6, and 12 volts. 6V and 12V models are used primarily in automobile lamps and are not installed in household products.
There are 2 connection methods:
- to the voltage source, required ;
- to a current source, called a driver.
In the first option, the voltage is stabilized; it should exceed the drop voltage across the diode.
Example.
If the drop is 3V per 1 LED, and at 12 volts, then to turn on 1 diode with a rated operating value of 0.1 Ampere, we get the following calculation:
- 12V – 3B = 9V
- 9V / 0.1A = 90 Ohm

In the second option, the current strength is stabilized and the connection diagram will be the same as in the first option, only you need to exclude the resistor. Ice chips with the same rated current when connected in series are selected. If the driver current is too high, and you really need to turn it on, then you can use parallel circuit. With this scheme in each chain there will be a multiple reduction.
Many people mistakenly think that if they are connected in series, the power consumption will remain unchanged, because the current will not need to be increased. They forget that they will have to increase the supply voltage.
LED designation on the diagram

Indicated in the diagram by two types of pictograms. Two arrows show that it emits light.
Characteristics

Before calculating the LED connection diagram, make sure their parameters and quality. The Chinese very often cheat by slipping in LEDs with different parameters or lower power. The Chinese are especially good at cheating with SMD 5630 and SMD5730; their well-known power is 0.5W. The numbers 5630 and 5730 indicate only the case size, for example, 5.7mm by 3.0mm.

Taking advantage of this, they install a 0.07W - 0.1W crystal in a standard case and then sell them as 0.5W. That is, the luminous flux will be 5 times less than you expected. A good example would be LED corn lamps, which are simply studded with low-power LEDs in quantities from 20 to 130 pieces. Due to this appearance, corn in the eyes of the buyer seems more powerful than a diode lamp with 10 diodes of similar energy consumption.

They also make copies of well-known manufacturers, especially Cree and Philips. They are similar to real KRI and Flips only in appearance, technical characteristics are 30-40% worse.
Assembly steps

Approximate sequence of assembly and testing in operating mode.
- find the technical specifications in the documentation, how many volts drop on each LED;
- draw up a connection diagram taking into account the supply voltage;
- calculate the power consumption of the entire electrical circuit;
- select a power supply or driver suitable for power;
- calculate the resistor when using a stabilized voltage supply;
- find the correct polarity on the LED legs;
- solder the wires to the diode components;
- connect the power supply;
- place the diodes tightly on the radiator and secure them;
- we turn on the entire structure to the 220V network after closing our eyes;
- if nothing exploded, then we measure energy consumption, heating, current consumption;
- we adjust the current if it turns out to be higher or lower than the calculated one;
- warm up for 30 minutes
- for Chinese diodes, the temperature at the electrical contact should not exceed 60°; for branded ones, this is indicated in the specifications; it can be a maximum of 130° - 150°.
 Aluminum star
Aluminum star
Installation on a cooling system most often requires good equipment and skills. Therefore, it is better to buy low-power diodes 1W, 3W, 5W directly on an aluminum or copper substrate in the form of a star. This way you will not overheat the legs and damage the diode chip. The star is then placed on the radiator using heat-conducting paste.
To solder wires to a star, you need a more powerful soldering iron, because aluminum quickly absorbs heat from the point of contact with the solder.
Power supplies

To connect super bright LEDs A current-limiting resistor must be used for a constant stabilized voltage. If the power consumption is more than 10W, it is not rational to use it.
The most common ones have the following power:
- 0.5W in SMD housing;
- 1W, 3W, 5W in case Emitter, round with legs;
- square COB diodes from 5W, 10W.
The most common stabilized sources:
- 1.5V – AA batteries;
- 3.7V – lithium batteries from phones;
- 5 Volts are USB chargers for smartphones and tablets;
- 9V – Krona battery;
- 12 volts – vehicle on-board network, power supplies from consumer electronics;
- 19V – power supplies from laptops are well stabilized and deliver up to 90W.

To reduce the number of volts from the power source, you need an adjustable stabilizer. I usually buy them on Aliexpress for an average of $2 for 2 Amp models, and $5 for a powerful 5 Amp module. In Russia the price for them is too high, it is better to buy in advance, but 2-3 times more.
Connection to a 1.5V battery

To connect a diode directly to a 1.5V battery, an increase to 3V is required. This is implemented on small specialized chips. Most often used in rechargeable flashlights on one AA battery. The microcircuit can be an Ampere stabilizer or increase only volts. If only the voltage is stabilized, then to turn on the diode you will need to install a resistor, which also consumes energy. The LED driver is more economical for a flashlight.
Chinese for 100 rubles. They sell ready-made boards with stabilizers, which from 1.5 can make from 2V to 5V. Those who are comfortable with a soldering iron can do it with their own hands; the microcircuit requires practically no additional elements.
Powered by 5V

The most popular source, every home has several chargers and a bunch of old push-button phones. At 5V you can only connect one in parallel. A minimum of 6V is required for serial connection.
A good example would be a 5V LED strip. I use this tape and old chargers to make LED night lights. A piece of tape 3-4 cm long is glued to the case and connected to the USB socket. If the case is collapsible, then I solder the wires inside, directly to the board.

 5V LED strip powered by USB
5V LED strip powered by USB
Switch on 9V
 9V Krona battery and brightness control
9V Krona battery and brightness control
The most well-known source of nine volts is the Krohn battery. Despite its small size, it has a very small capacity. Nine volts will allow you to switch up to 3 iner in series. If 3 pieces are connected in series, then a small decrease will lead to a significant decrease in brightness. If it is impossible to ensure good stabilization, then you will have to reduce it to 2 LED chips.
To adjust the brightness, you can use a miniature dimmer, the price of which is 50 rubles.
How to connect an LED to 12 volts
 12V stabilizer
12V stabilizer
12 volts already provides ample switching possibilities. The LED connection diagram can be 3 in series. Four pieces are not included in this way, because the voltage drop under load should be taken into account. For example, it may drop from 12V to 11V, which will lead to a significant loss of luminous flux.
It is best to use a low voltage driver to avoid using a resistor. This stabilizer operates from 12V and has an output voltage regulator and an Amp setting. In addition, its design is simpler than 220V and does not have a transformer, only a choke.

An example would be a 12V LED strip in which 3 LEDs and a resistor are connected in series.
In the car network, including the cigarette lighter, when the engine is running, there is from 13.5V to 15V. But surges can be up to 30V. When the car is turned off, it will be from 12V to 13V, depending on the charge level of the car battery. Therefore, it is highly not recommended to turn on LEDs without a stabilized power supply or current stabilizer. Chinese ones tolerate such surges very poorly, due to the low quality and poor conductors of the crystal. Branded Cree Philips Osram types can work for a long time in a car even without a stabilizer, this has been tested on LED lamps ah for side lights.
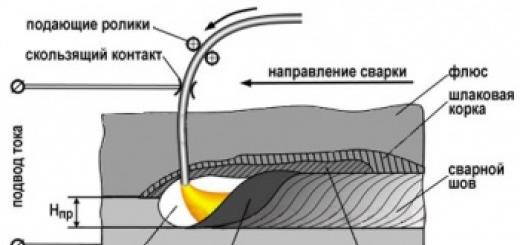
How to connect an LED to 220V
 LED driver for 100W and 50W
LED driver for 100W and 50W
To connect an LED to a 220V network, the circuit uses specialized power supplies, which may be called led driver, current source, power supply, stabilizer. Its main characteristics are current in Amperes and power. The driver can have a fixed output current or an adjustable one. If you assemble the lighting device with your own hands, then it will be more convenient with a regulator.
Typically, ice chips are connected to the driver in series, which guarantees the same current through each element of the electrical circuit. The disadvantage of this scheme will be the failure of the entire circuit if 1 ICE burns out.
The driver circuit for LEDs can be different, from a simple one with a quenching capacitor to a modern one, with a light flux pulsation coefficient close to 0%.
A classic example of such a design is a 220 LED lamp. To modernize old lamps, I sometimes use the filling from a light bulb. I place a plate with LED elements on the heat sink inside the lamp and place a stabilizer next to it. Such modernization is relevant when upgrading non-standard fluorescent lamps.
Now it has become easy to connect an LED to 220; it is more difficult to determine the pulsation coefficient of the light flux. If the driver is of poor quality and does not cope well with the load, the light will flicker at a frequency of 100 Hertz. The reaction to these pulsations is individual for each person. Most often it leads to headaches, eye fatigue and a long list of other negative consequences.
Connection to 220V without driver

An example of a simple switch on without a driver would be a 220V LED strip. There are 60 pieces connected in series on it, which are powered by a rectifier consisting of a diode bridge. The disadvantage of this scheme is the pulsation of light with a frequency of 100 Hertz, which is very harmful to health, but everyone reacts to it individually. This tape can only be cut into 60 LED strips.
 LED strip with direct connection to the network 220
LED strip with direct connection to the network 220
The same technology began to be used in large COB diodes; 60 crystals are connected in series inside to be immediately connected to a 220V network.

High-tech Chinese are already selling LED modules and matrices with a stabilizer placed on the same substrate.
RGB LEDs and color

Other characteristics include LED for plants and color ones; the manufacturer must indicate their exact parameters upon purchase. There are several types of monochrome:
- Red light;
- blue;
- green;
- yellow;
- ultraviolet;
- infrared.

The voltage drop across the chip depends on the light emitted, so they have different power consumption. For example, for red ones the drop in volts will be 2 - 2.2V. Therefore for each color RGB LED you need to calculate the resistor separately on a calculator. The RGB crystals are not covered with a yellow phosphor, so the crystals and their connection diagram are clearly visible through the transparent silicone coating.

Energy-saving technologies and equipment are in demand and popular. One such device is an LED lamp. It uses LEDs as a light source, which are combined into one circuit. This light bulb is used in lighting fixtures to decorate the illumination of buildings and structures, in spotlights that are mounted on suspended or suspended ceiling structures.
Design of LED lamps
LED lamps are designed for a voltage of 12 V and, accordingly, the design of the device differs from its fluorescent counterparts or those that use an incandescent filament. Structurally, it is made of the following main components:
- Glass flask. It can be made of transparent or frosted glass and have a spherical or flat shape. The dome design increases the light dispersion angle to 270°. Models of light bulbs with a flat glass surface are used in spotlights to illuminate the interior or divide the area into separate zones. Lighting angle 30 – 60°.
- LEDs. Light sources are connected in series into one connection circuit, which increases the light output of the device.
- Radiator. Represents metal plate made of aluminum alloy. It is designed to remove the heat emitted by the LEDs.
- Frame. It is made of high-strength plastic, which is a dielectric and performs protective functions against electric shock when installing or dismantling the light source.
- Driver. Designed to stabilize voltage and convert current from alternating to direct.
- Base. Can be made for cartridges different types A: standard design E27 and E14 or G4, G13, GU10 and so on.
Depending on the amount of light emitted by one diode and the number, the brightness of the LED lamp is determined. The average illumination value is calculated from the ratio of 1 Lm (Lumen - a unit of measurement of the brightness of a luminous flux) per 100 W.
Advantages and disadvantages of 12V lighting
To switch to lighting fixtures that connect to a low-voltage power source, you should study their advantages and disadvantages. Among the advantages are the following:
- Safety. The use of LED lamps in 12V luminaires increases the level of protection and eliminates the possibility of electric shock.
- Fire safety. Low voltage wiring cannot be a source of ignition or cause a fire. Therefore, the wires do not need additional protection; they are not placed in corrugated sleeves.
- Versatility. Electricity the voltage of which does not exceed 12 V is considered conditionally safe, which cannot cause serious harm to a person. In this regard, these lamps can be used in rooms with normal conditions and increased danger. For example, in lamps for a sauna, cellar, bathroom, kitchen, bedroom, etc.
- Saving. Using this source lighting the room reduces energy consumption and, accordingly, the cost of money to pay bills.
- Environmental friendliness. The design does not use materials that, during operation of the device, emit substances harmful to human or animal health.
- Reliability. The lamps are highly resistant to mechanical damage: scratches, chips, dents, etc.
Despite all the advantages, the light source also has its disadvantages. The disadvantages of LED lamps designed for 12V include:
- An additional device is required - a power supply unit (PSU). The presence of a driver that stabilizes and reduces the network voltage from 220 to 12 V complicates the wiring. It has its own efficiency, which reduces the efficiency of lighting and due to it, an additional weak link appears in the circuit, which can fail.
- Glow brightness. The luminous flux power of a lamp connected to a low-voltage network is affected by the voltage drop. This occurs due to high current consumption. Therefore, the length of the conductor from the transformer to the first and last light source must be the same, an error of 2 - 3% is allowed. Otherwise, the last lamp will shine dimmer than the first.
Types of LED lamps
Light sources are classified according to several criteria:
- Base type. Available in traditional versions with standard sizes: E14, E27, E40. Baseless lamp models are also produced: G4, G5, G9, etc.
- Glow temperature. There are three types of emitted light: soft - temperature from 2500 to 2700 °K, white - 3800 - 4500 °K and cold light temperature more than 5000 °K
- LED type. Depending on the power and purpose of the lamp, LEDs have different configurations, which are determined by the type of crystal. It can have legs for connection or be mounted directly into the board.

Power supply for 12V LED lamps
Power supplies are selected depending on the purpose of the LED lamps.

They are divided into the following types:
- Sealed. Used for installing lamps in the bathroom, sauna, and street lighting.
- Leaky. Designed for indoor installation with normal humidity levels.
- With active cooling. It is equipped with a fan, which increases power and reduces size.
- Passive cooling. A radiator is used to remove heat. The advantage is silent operation. Disadvantage: power is limited by the size of the device.
Also, power supplies are selected according to their main characteristics:
- Power. It is calculated by adding the entire connected load plus a power reserve of 10 - 15% to prevent operation in overload mode.
- Output current. Depends on the number of connected lamps. If the load power and the “cosine phi” of the lamps are known, then the current can be calculated using the formula: total power of the lamps / 12 / cos φ. The value of the parameter also determines the cross-sectional area of the conductors connecting the power supply and lamps.
- Output voltage. For our case it is 12V.
When connecting 12V LED lamps to a 220V electrical line, they must be powered by a driver or power supply.
Technical progress in the field of energy-saving technologies contributes to the constant development and improvement of the technical and operational characteristics of LED lamps.
Video on the topic