Some types of metals cannot be welded using conventional welding. If electrodes are used, the seam is not strong and cannot provide a tight connection. For non-ferrous metals, alloy steel and alloys, TIG welding is required.
- How does the argon welding method differ from others?
- What does the technology of welding work using the protective atmosphere of argon include?
- What safety measures will need to be followed?
Tig welding technology
Performing welding work has always required a certain specialized education. But modern technologies have made it possible to simplify this process so much that, thanks to special equipment, it is possible to obtain high-quality results even at home. The operating principle of argon-arc welding is also simple, which allows it to be used even by non-professional workers.The main difference between welding with argon and the conventional electrode method is that the work is carried out using a protective cloud created with argon. In this case, the temperature in the arc column reaches 2000°C, which allows the use of tungsten non-consumable wire as the main consumable material.
Other features of the technological process are:
- The electrode must be positioned as close as possible to the surface of the metal being processed. This makes it possible to ensure the required temperature of the weld pool during argon-arc welding and ensure the required weld thickness and penetration depth. The further the electrode is from the metal, the lower the quality of the applied seam.
- Direction of movements - it is necessary to guide the electrode along the seam. The absence of oscillatory movements helps create an aesthetically pleasing seam. At the same time, practice is required from the master to create all the necessary conditions for sufficient penetration.
- The essence of the technological processes of argon-arc welding is to ensure that at the moment of applying the seam it is not exposed to oxygen and nitrogen released during the combustion of the metal. It is necessary to ensure that the electrode and filler material are constantly in a protective cloud of argon.
- The wire feed speed should be uniform. There should be no jerks that cause metal spattering. The technique of electric arc welding in an argon environment involves a sequence of actions by the master: the correctly selected angle of supply of the filler wire in front of the torch, strict adherence to the direction of application of the weld and precise settings regarding the intensity of the gas supply to the torch.
- Welding speed - the weld is applied slowly. In this case, it is necessary to take into account possible metallurgical processes inherent in this processing method. For example, gas supply to the surface of the part should begin for 10-15 seconds. earlier, but will end 7-10 seconds after applying the weld. The crater is welded using a rheostat (reducing the current on the arc). Calculation of argon consumption during welding is carried out using special tables and standards. The main provisions can be found in GOST 14771 76.
The master learns most of the nuances associated with performing work through practice. Some help can be obtained from special reference books and manuals for welding in shielding gases. Equipment manufacturers also try to interest potential buyers and provide a lot of useful information and calculations of welding modes in the operating instructions.
Features of the argon-arc welding technique lie in the correct combination of: wire feed, exposure to a tungsten electrode, argon supply intensity and weld application speed. It will become easier to regulate all these components as you gain experience.
Equipment for argon arc welding
Welding work in a protective gas environment is carried out using both proprietary installations designed directly for argon-arc welding, and modified devices used for other work. In any case, the use of special equipment is required, each of which has its own purpose. Namely:Practice has shown that it is easier for novice craftsmen to achieve the required quality using an argon-arc welding inverter. The inverter produces a stable arc, which facilitates the process of applying a weld.
Automatic argon arc welding
To facilitate the work process, automatic argon arc welding with a non-consumable electrode is provided. The consumer can purchase an installation with different automation levels. It is customary to distinguish the following settings:
Mechanized welding is used most often in Russia. Therefore, when performing welding work, the human factor plays a great role, namely the qualifications of the craftsman.
Filler materials for argon arc welding
Filler rods for argon arc welding are used to fill the weld pool when argon is supplied. This material is used when processing metals with properties that complicate the application of a seam. Depending on the characteristics and composition, electrodes for welding in argon may be required when working with cast iron, aluminum, nickel, titanium and other non-ferrous metals, as well as alloy and heat-resistant steel.Depending on the base material, the following additives are distinguished: 
Welding wire for argon arc welding of stainless steel has its own characteristics that are taken into account when working with this material. It is especially important to ensure that the weld pool does not extend beyond the protective argon cloud.
Manual argon arc welding technique
The process of performing the work is quite simple, you can learn it yourself. If you have high-quality equipment for manual argon arc welding, applying a seam will not be difficult even in domestic conditions. When welding in argon manually, you will need to follow certain recommendations:- The suture should be applied exclusively in the direction of the lump being treated. Oscillatory movements thicken the seam and reduce its strength.
- It is necessary to ensure that the arc moves at a sufficient speed. The craftsman is required to ensure the proper depth of metal penetration.
- High-quality manual argon arc welding with a non-consumable electrode depends on uniform wire feeding and setting the appropriate operating mode.
It is most convenient to perform manual welding using inverter equipment with mechanical supply of filler material.
How to cook using argon arc welding
For argon-arc welding, the following conditions must be met:
Scope of argon arc welding
The technological process of the work makes it possible to use this method for the repair and manufacture of parts and structures of any non-ferrous metals and refractory steels. Currently, thanks to the features of the equipment, welding work using the protective environment of argon can be carried out both in industrial conditions and at home.It is possible to roughly outline the scope of application of the argon welding method according to the type of metal being processed. Namely:
- Argon arc welding of aluminum - the difficulty of processing aluminum alloy using the conventional electrode method is that the metal has good thermal conductivity and does not change its color when heated. It is possible to ensure high quality welds on aluminum only in a protective gas environment. Welding aluminum alloys requires the use of filler materials; in this case, the wire will have a homogeneous composition.
- Stainless steel welding is another material that is difficult to process. The disadvantage of the electrode method in this case is that in the process of applying a seam on stainless steel it is necessary to overcome the oxide film. The work is performed using stainless steel wire or without filler material. The angle of the burner in the second case will be about 90° degrees. When choosing modes for argon arc welding of stainless steel, it is necessary to take into account that this metal is prone to cracking, therefore it is required that the weld cools slowly with a constant supply of gas.
- Argon arc welding of cast iron is the optimal solution to the problems of repairing both plumbing pipes and other products. It can be used for minor repairs of defects in cast iron surfaces that arose during the casting process.
- Welding titanium in an argon environment is practically the only way to process titanium alloys. The difficulty is that even when heated to 450° degrees, titanium forms oxide and scale saturated with oxygen. This promotes the formation of cracks and does not allow a high-quality weld to be applied in any other way. When welding titanium, special pads are used to facilitate the supply of argon from the back side of the workpiece.
- Carbon steels - there are special processing features for these metals. The welding mode for carbon steels involves the use of forging the seam when it reaches a hot temperature and ensures slow cooling of the surface being processed.
- Copper - a feature of copper is its high thermal conductivity. Therefore, argon-arc welding of copper is performed under the condition of an increased argon supply of about 150-200 l/hour.
Safety precautions for argon arc welding
Carrying out work using a protective gas environment is regulated in accordance with GOST 12.3.003-86. GOST contains requirements for industrial use, but it is recommended to comply with them in domestic conditions.First of all, restrictions are related to harmful substances generated during the work process and other potentially dangerous situations.
Some provisions of this GOST are given below: 
A welding mask or special glasses are a prerequisite for performing work. Chameleon masks have proven themselves well. Welding helmets with chameleon glasses independently change darkness depending on exposure to radiation.
Components and consumables
In addition to purchasing the installation, you will need to buy consumables for argon-arc welding and constantly monitor their availability and serviceability. So to complete the work you will need:- Welding mixture - although the main percentage is argon, it is not supplied to the torch in its pure form. A high-quality argon mixture contains from 10 to 50 percent carbon dioxide in its composition. It is permissible to use formulations with helium. Before purchasing, you should check with your consultant for what purpose the mixture is used.
- Cylinders - can be reused. From time to time it is necessary to check the cylinders for depressurization. Some service centers can fill the required mixture into already purchased cylinders. Since some metals require high gas consumption (copper will require a flow rate of 150-200 l/hour), it is necessary to purchase components with sufficient volume.
- Hoses - you can buy welding hoses of various lengths and additional functions. Before purchasing hoses, you should make sure that the selected hose is suitable for the welding installation. The argon arc welding sleeve is connected to the gearbox.
- Reducer - controls the flow and supply of argon. The reducer is installed on the cylinder and automatically lowers or increases the pressure when working with certain types of metals.
Disadvantages of argon arc welding
Like any method, argon arc welding has its disadvantages. These include:- A large amount of additional equipment used.
- The difficulty of selecting the correct mode of work. For a novice master, choosing the necessary parameters is extremely difficult. When working with some metals, pulse welding is required; for others, the weld is applied using a spot method intermittently. It may be necessary to use DC or AC voltage.
- Inability to fully protect the seam in drafts or strong winds.
Despite these disadvantages, the method of welding in argon also has its positive aspects.
Advantages of argon arc welding
The choice of TIG welding should be influenced by advantages that cannot be achieved by any other metal processing method. Namely:- Slight heating of the metal surface. For titanium and cast iron and other non-ferrous metals, strong heating is critical. Using the welding method using argon allows you to perform high-quality welding work.
- High speed of work.
- Possibility of processing metals that cannot be welded in any other way.
- High-quality, smooth and thin seam.
- Ability to perform work at home without specialized education. According to statistics, the majority of those who choose an argon arc welding machine for their home are not specialists.
The possibilities of argon arc welding are almost limitless, and the welding technique is so simple that it allows you to perform the work even without specialized education and practice. This is what explains the popularity of the equipment.
The stainless steel category includes high-alloy steels with pronounced resistance to corrosion. The main alloying component in these materials is chromium. Depending on the class of stainless steel, it may contain up to 20% of this alloying element. In addition, steel may contain components that will increase its anti-corrosion characteristics and impart certain physical and mechanical properties. Such elements include titanium, nickel, molybdenum, etc. Stainless steel and aluminum are among the materials whose cooking requires compliance with certain conditions. Before you do, you should familiarize yourself with some of its features. Both aluminum and stainless steel can be cooked with argon. Before cooking with argon, you need to familiarize yourself with the characteristics of the material being processed and prepare it for work accordingly.
Argon welding is a high-tech process that allows you to obtain high-quality welds when performing small volumes of welding work.
What should you consider when cooking stainless steel with argon?
Before cooking with argon, study the following important properties of aluminum and stainless steel. Thus, stainless steel has almost 2 times less thermal conductivity than low-carbon steels. As a result, the heat concentration during the welding process will increase, followed by an increase in the penetration of the material at the joint. This property of stainless steel necessitates the need to reduce the current strength by an average of 20% when compared with the same indicator when working with conventional steels. Stainless steel, like aluminum, is characterized by a fairly large coefficient of linear expansion. When welding stainless steel products, due to this property, significant casting shrinkage is observed. It leads to increased deformation of the material during welding and after it. If there is not enough clearance between the stainless steel or aluminum workpieces being welded, significant cracks may appear.

Stainless steel and aluminum are characterized by high electrical resistance. When working with such materials with electrodes made of high-alloy steels, the latter will become very hot. To eliminate the negative effect, chromium-nickel electrodes are available in lengths up to 35 cm.
Stainless steel loses its high anti-corrosion ability when worked in the wrong thermal conditions. This phenomenon is known as intergranular corrosion. The physicochemical nature of the phenomenon boils down to the fact that when the temperature rises to 500°C or more, chromium and iron carbide begins to form at the edges of the grains. Subsequently, these grains become centers of corrosion. You can get rid of such an unpleasant phenomenon in different ways. One of them involves rapid cooling by any available methods, including simply pouring cold water over the material being welded, in order to reduce the decrease in corrosion resistance to a minimum. However, it is important to consider that aluminum cannot be cooled with water, and in the case of steels, this method is only suitable for chromium-nickel austenitic materials.
How to prepare stainless steel for cooking?
Both aluminum and stainless steel require proper preparation before work. There are several ways to weld stainless steel. The most widespread are the following:

- Work using coated electrodes.
- Application of tungsten electrode.
- Semi-automatic welding mode using stainless wire.
Each of these methods has its own characteristics and is suitable for performing a specific list of work. In the process of cooking stainless steel with argon you will need:
- Welding machine.
- Electrodes. Selected in accordance with the characteristics of the material being processed.
- Stainless steel wire.
- Steel brush.
- Solvent.
Before welding parts, you need to process their edges. This is done in almost the same way as in the case of working with low-carbon steels. There is only one peculiarity: in order to ensure free shrinkage of the seam, when creating a welded joint, you need to make some gap. Of course, within reasonable limits.
Before work, you need to clean the surfaces of the edges. To do this, use a steel brush. The edges also need to be washed with solvent. Acetone or aviation gasoline will do. This treatment allows you to get rid of fat and is mandatory. Indeed, in the presence of fat, the stability of the arc will decrease and pores will begin to appear in the seam.

Welding stainless steel using coated electrodes allows you to obtain seams of normal quality without any problems. Therefore, if you do not have very high demands on the quality of the connection, then choose this particular welding method.
There are quite a few types of electrodes, each of them is suitable for working with stainless steels of a certain composition. All this information is provided in GOST. Knowing the grade of steel being welded, you can easily determine which electrodes need to be used to work with it. Choose electrodes that will not reduce the corrosion resistance of the material and spoil its mechanical characteristics.
As a rule, work is carried out using a reverse constant level. You need to try to do everything so that the seam melts as little as possible. Use small-diameter electrodes for work. It is necessary that a minimum amount of thermal energy is released. It was previously noted that when working with stainless steel, you need to use a current 15-20% weaker than when welding plain steel, do not forget about this.
The electrodes have low thermal conductivity and high electrical resistance. Because of this, high currents cannot be used. If this rule is violated, the electrodes will overheat and be destroyed. For the same reasons, electrodes for stainless steel melt faster than those used to weld ordinary steel. And this usually surprises inexperienced welders.
To maintain the corrosion resistance of the seam, everything must be done to ensure that it cools as quickly as possible. For example, you can cool it with copper pads or air. If the stainless steel you are processing is classified as chromium-nickel austenitic, you can even cool it with water.
Tungsten welding instructions

This mode is used in cases where it is necessary to weld products from very thin stainless steel or to obtain a high-quality welded joint. For example, argon welding using tungsten electrodes is best suited for stainless pipes that transport gases or liquids under pressure.
Work is carried out on alternating or direct current. Variable is suitable for working with aluminum. The polarity of the current is straight. Argon is used. Before you start welding, you should prepare the filler wire for work. It is better if it has a higher degree of alloying than stainless steel or aluminum.
When working with an electrode, you must not make oscillatory movements: because of this, the protective space of the welding zone will be disrupted and the weld metal will oxidize. The reverse side of the seam must be protected from air by blowing argon.
When working, try to ensure that no tungsten gets into the weld pool. You can use non-contact arc ignition. It can also be ignited on a coal or graphite plate with further transfer to the base metal.
When welding work is completed, there is no need to turn off the argon supply immediately. Do this after about 15 seconds. This will prevent excessive oxidation of the heated working electrode. This way it will last much longer.
How to cook stainless steel semi-automatically in argon?
This welding method is the most preferred. It ensures the highest possible productivity and produces very good quality seams. In order to improve the quality of welding, nickel is added to the wire.
The semi-automatic argon welding process for stainless steel is best suited for joining thick materials. In this case, the welding speed will be maximum. Consequently, productivity will also increase. The protective environment in such conditions is a mixture of carbon dioxide and argon. Due to carbon dioxide, wettability at the edges of the seam increases.
There are several techniques that allow, namely:
- Short arc welding.
- Working with jet transfer.
- Pulse mode.
Jet transfer is suitable for welding thick metals, while short arc is suitable for thinner products.
Among the advantages of the pulse mode is that it is the most controlled process. The wire metal is pulsed into the weld pool. Each of these pulses is a separate welding drop. This mode allows you to reduce the average value of the arc current, which is very important when working with stainless steel, because heat input and heat affected zone are reduced.
In addition, the pulse mode almost completely eliminates metal splashes. This allows you to significantly save consumables and increase productivity by reducing the time required to clean a seam.
Thus, there are several modes for cooking stainless steel with argon. Choose the one most suitable for your case. Good luck!
Copper, etc.) which practically cannot be joined using traditional equipment, therefore argon-arc welding is successfully used to create one-piece structures from these materials. Do-it-yourself argon welding is carried out using standard equipment or using a home-made unit and requires certain skills and knowledge, without which the process is doomed to failure. Argon welding torch
Features of argon arc welding
In argon-arc welding, the process occurs in an inert gas environment (argon), which protects the mating surfaces from oxidation, thereby improving the quality of the weld. can be carried out in manual and automatic modes using a non-consumable and consumable electrode.
A tungsten element is usually used as a non-consumable electrode in argon-arc welding, since it is a very refractory material. Using this welding method, it is possible to reliably join materials that are very difficult to weld using traditional methods, and even dissimilar parts.
Features of technology for argon arc welding
To work confidently and productively, you should know how to weld with argon and adhere to some rules, the implementation of which will greatly facilitate the process and allow you to achieve high-quality welds.
Do-it-yourself argon-arc welding involves creating a strong and reliable seam, and therefore requires increased attention when carrying out work.
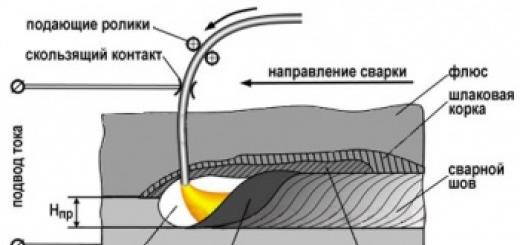
- The non-consumable electrode should be kept as close as possible to the surface to be welded, creating the shortest possible arc length. As the arc increases, the depth of metal penetration decreases and the width of the seam increases, that is, quality suffers.
- Typically, during argon-arc welding, only one movement is performed, which is directed along the axis of the seam. The absence of frequent transverse movements makes it possible to create a narrower and aesthetically attractive seam, which distinguishes this technology from the use of coated electrodes.
- To prevent saturation of the welded surfaces with nitrogen and nitrogen contained in the air, care should be taken to ensure that the non-consumable electrode and filler wire are in the argon protection zone.
- When the welding wire is fed sharply, active spattering of metal is observed. To prevent this process, the wire should be fed very smoothly, which can be achieved with practice.
- One of the indicators of the quality of a weld is its penetration, which can be judged by the shape formed by the weld pool. Good penetration can be judged by a weld pool that is elongated towards the welding direction, while an oval or round shape indicates insufficient surface penetration.
- When welding with a non-consumable electrode, the filler wire should be placed at an angle to the surface to be welded in front of the torch, avoiding transverse vibrations. This way it is easier to ensure an even and narrow weld seam.
- The crater is welded at the end of the work by reducing the current strength with a rheostat (it is incorrect to stop work by breaking the arc, retracting the burner, since the protection of the seam is sharply reduced). Typically, the supply of gas (argon) is stopped 7 - 10 seconds after completion of work, and the supply of gas to the connection area should be started 15 - 20 seconds before the start of the process.
- Before starting welding work, the surfaces of parts should be cleaned of oxides and dirt by mechanical or chemical means, and also degreased.
 Argon welding principle
Argon welding principle Mode parameters for argon-arc welding
Do-it-yourself argon welding will take place at a high level if you choose the optimal modes that will ensure the most efficient process.
- The polarity and direction of the current are selected according to the properties of the metal being welded. Typically, when working with basic steels and alloys, direct current of straight polarity is used. It is preferable to weld aluminum, magnesium and beryllium with reverse polarity, which promotes faster destruction of the oxide film.
- The set welding current depends on the brand and composition of the materials, the diameter of the tungsten electrode, as well as the polarity of the current. The exact mode data for solving a specific problem should be selected from reference materials or based on your own experience.
- The voltage of the arc depends entirely on its length, so it is recommended to carry out work by creating a minimal arc, achieving a reduction in voltage. As the arc length increases, the tension increases and the quality of the seam deteriorates.
- The flow rate of inert gas should be set in such a way as to create a laminar flow that will completely protect the surfaces being welded from oxidation.
 Metal welding modes
Metal welding modes Selection of optimal modes is a rather complex process, therefore argon-arc welding training should be carried out by an experienced specialist who has both theoretical knowledge and practical skills in performing such work.
Upgrading a conventional welding machine to use argon
Often, do-it-yourself argon welding is carried out using a non-standard one, that is, a machine modified to solve specific problems. To ensure the quality of work, two additional units will be needed that will help carry out the process at a high level of quality.
- An oscillator is a device used to ignite an electric arc without contact. It maintains a stable arc discharge when operating in modes requiring the use of alternating current. Since ignition of the arc during argon-arc welding for a number of reasons is impossible by directly touching the working surface with the electrode, the oscillator generates a high-voltage discharge (4 - 8 kW), which breaks through the arc gap.
- The ballast rheostat is used to regulate the current strength and select optimal parameters when welding parts made of various materials. When welding aluminum using alternating current, it is recommended to regulate the rheostat within very narrow limits (15-20%), since it will still not be possible to compensate for the direct current component.
Advantages and disadvantages of argon arc welding
You can become more familiar with the process by watching argon-arc welding (video), which shows techniques for setting up equipment and methods for mating various surfaces.
Advantages:
- the heating area of the base metal is very small, which preserves the original shape of the workpieces;
- argon is an inert gas, the specific gravity of which is heavier than air, so it reliably protects the welded surfaces from environmental influences;
- high thermal power of the arc allows you to increase the speed of work;
- the simplicity of the technical techniques makes this welding method generally available;
- the ability to weld parts that cannot be connected in any other way, obtaining a neat and aesthetic seam.
Flaws:
- the possibility of incomplete protection of seams when working in strong winds or drafts, since some of the argon may not reach its intended destination;
- when carrying out work with a high-ampere arc, it is preferable to use additional cooling;
- quite complex equipment used for the job and some difficulty in fine tuning.
For a more detailed introduction to the process, you should watch how to cook with argon (video), which clearly shows all the features of the process, and also familiarize yourself with the necessary equipment.
The problem of quickly connecting metal workpieces ceased to exist after the invention of short-circuit arc welding, progress did not stop there, and was invented. Lightweight and powerful inverters avoid exposure to oxygen on the weld; this can be achieved by using inert gas during the welding process. This method is used to cook metals and alloys, including those that oxidize quickly, which cannot be combined in any other way. We will talk about this process, find out what is needed for it and discuss the technology of argon arc welding using inverter machines.
The most popular, according to many reviews, are inverter welding machines, which weigh little, have sufficient power and capabilities such as welding in an argon environment. They are inexpensive and with the purchase of a torch and cylinder they acquire very wide capabilities, allowing you to weld aluminum alloys, titanium, stainless and alloy steel. There are many varieties of welding wire and rod that give the weld strength and high quality joints even between dissimilar metals. The only obstacle is the aggressive effect of oxidizing atmospheric oxygen, which is eliminated by the inert gas environment.
Simple training allows you to quickly acquire the necessary skills, and the cost of the equipment will quickly pay for itself because the cost of such work when ordering from third-party workshops is extremely high. In order to understand how to cook with argon correctly, you need to know the working methods and equipment that allows you to perform such operations. For these purposes, the following techniques are used:
- inverter welding in a protective environment using the TIG method using a refractory tungsten electrode and manual wire feeding into the welding zone;
- semi-automatic welding using the MIG method with the supply of melting wire into the weld pool at an adjustable speed.
The least expensive is argon-arc welding using the TIG method, since MMA + TIG inverters are more affordable, but usually do not include a torch and gas supply hose. You will also have to purchase tungsten electrodes and filler wire, which is fed manually into the welding zone. The high versatility of the method allows you to weld aluminum alloys, stainless steel, cast iron and sheet metal, which is necessary when repairing car bodies.
More expensive MIG/MAG equipment makes it possible to automatically feed welding wire of various thicknesses at an adjustable speed into the melting zone. This wire is the electrode, and it is selected that is closest in composition to the parts being welded. The feed is carried out from a special built-in drum through a Euro-sleeve to the torch, which is equipped with nozzles of various internal diameters for the passage of wire. With this equipment, both argon and active gas welding are possible.
It is important to note that work using inert gases must be carried out in rooms where there are no drafts in order to avoid excessive gas consumption and deterioration of the quality of the seam.
Equipment for argon welding
Joining metals and alloys has been a major engineering challenge for hardware designers for a long time. The first experiments, naturally, were related to the defense industry, but progress in this area suggested the civilian use of argon for welding for ordinary everyday purposes. The consumer has the problem of welding dissimilar and quickly oxidizing parts in the open air, and here argon welding is a way out of a difficult situation. It should be noted that this type of work requires certain, not very expensive equipment that ensures the proper quality of the weld, namely:
- gas cylinder, with two reducers and pressure gauges to ensure the supply of inert gas or mixture to the weld pool area;
- connecting hose for supplying the mixture to the zone of molten metals or alloys with a sealed connection;
- burners for various purposes using the TIG or MIG method, but providing the supply of inert gas to the melting zone of the metal or alloy.
- Euro connector for various purposes;
- tungsten electrodes (TIG) or welding wire (MIG) to ensure a trouble-free process;
- welding oscillator built into the inverter for high-frequency excitation of a short circuit arc.
The gas cylinder is used to supply gases through reducers, which ensure the supply of the mixture in the required proportions to the melting zone of the weld pool. To ensure this process, one or two gas cylinders and pressure gauges are used. The gases are mixed for steel and aluminum alloys at 99.98% argon, 0.01% nitrogen and 0.002% oxygen. Helium is also often used, which provides a high melting temperature of materials and deep welding of the seam.
The connecting hose in the TIG method is used as a way to supply inert gas to the place where metals are welded. The MIG method uses a Euro-sleeve, which, in addition to supplying inert gas, serves as a channel for moving the welding wire into the melt zone. The torches have different design features, and if in the TIG method it is a ceramic holder of a tungsten refractory electrode with an inert gas supply nozzle, then the MIG method also serves to supply the welding wire to the melting zone.
It is important that tungsten electrodes need cleaning because contaminants significantly deteriorate the quality of welding of metals and alloys.
Purpose of argon welding and materials to be welded
You can understand what argon welding is by looking at the example of connecting aluminum and bronze workpieces, which cannot be welded using conventional electrode arc welding under any circumstances. The goal of welding technology at this level is to isolate the weld pool from the effects of oxygen, which forms an oxide film, and to connect, for example, stainless steel into a single whole. Trained and experienced welders know how to weld complex alloys, cast iron and titanium with argon. We will talk about the possibilities of argon arc welding using the example of joining various metals and their alloys, as well as sheet metal, namely:
- you can cook cast iron, structural steel and sheet metal under argon;
- stainless metals, including food and medical purposes;
- aluminum alloys with appropriate wire and additives;
- titanium, copper, as well as galvanized steel, bronze and other alloys.
A neat seam on titanium, stainless steels and sheet metal can only be achieved by welding under argon, but even in this case maximum cleaning from contaminants, oils and the oxide layer will be required.
The inverter creates a pulsed high-frequency current, which, together with an inert gas, allows you to destroy the oxide layer and makes it possible to obtain a thin and strong welding seam. This method makes it possible to join dissimilar metals, carry out car body repairs, weld thin galvanized sheets, and to save money, expensive argon can be combined with carbon dioxide. Inert helium is also used to work with pure metals and magnesium alloys, and nitrogen is preferred for copper alloys. All these protective gases are produced in varying degrees of purity up to 99.9% of the highest category, up to 99.5% of the first category and up to 99% of the technical category.
Argon welding technology and sequence of operations
Let's consider TIG welding technology using an inverter welding machine. Products of this kind are usually produced in the MMA + TIG configuration and have appropriate connectors for connecting gas hoses, and the burner is connected through a connector using a Euro hose. The welding sequence consists of the following steps:
- the valve on the cylinder is opened and the argon flow rate is set to 6 to 8 liters per minute, depending on the thickness of the metal and the welding current;
- if a mixture is used, it is used in a ratio of 80% argon and 20% carbon dioxide;
- a refractory tungsten electrode is attached to the burner, protruding 3-5 mm from the nozzle exit;
- the wire corresponding to the parts to be welded is selected, and the workpieces are fixed;
- the inverter is turned on and the welding process is started with the torch button, while the pulse from the oscillator arrives with a delay of 1-2 seconds;
- achieve the formation of a weld pool into which welding wire is manually fed.
Argon welding requires skill, acquired through training in courses or independently. If difficulties and questions arise, it is better to seek advice from specialists, or select a suitable operating mode experimentally.
When argon welding using the MIG method, it is necessary to use a welding wire placed on a drum with an adjustable feed rate through a Euro-sleeve into the arc area. The wire diameter (from 1 to 4 mm) is selected individually depending on the thickness of the parts being welded; the torch has interchangeable nozzles for different sizes. Argon is supplied a little earlier to avoid oxidation of the workpieces in the weld pool and to facilitate ignition of the short circuit arc. The consumption of wire, which is the electrode, depends on the speed of argon welding and is selected individually.
It is necessary to remember to use a Chameleon type welding helmet, protective clothing and gloves, and also follow safety regulations.
Conclusion
The capabilities of modern technology make the process of welding in an argon environment a more than accessible method of work. This process is not difficult to learn, and the benefits will be very noticeable because the costs of consumables are not very high. We hope that we could be useful to you by talking about argon welding using the two most popular methods.
How is stainless steel welded with argon? The entire technology process will be covered in this publication!
Belongs to high-alloy steels, resistant to rust. According to the chemical composition, it is based on chromium and chromium-nickel, and according to the metal composition it is divided into dispersion-hardening, austenitic, martensitic, austenitic-ferritic and ferritic.
Any of the steels listed contains at least 12% chromium, which has a positive effect on strength and workability.
Due to its excellent properties, stainless steel is widely used in everyday life and industry. Therefore, having the skill of welding such metal, you will save yourself from many household troubles.
The material has a number of nuances that you should know:
- low thermal conductivity increases the risk of burning through thin metal (treated by reducing the current);
- large shrinkage causes the formation of cracks (the correct gap between the workpieces is necessary);
- loss of anti-corrosion properties at the welding site of stainless steel (rapid cooling required).
To weld stainless steel, you need a power source with settings for: non-contact ignition and crater filling.
Filler rod must be of the same composition as the material being welded to ensure the weld is strong and corrosion resistant. For example, the widely used stainless steel is 304, which means the wire should be Y308. More clearly in the table:
To reduce gas consumption and better protect the weld pool, use a gas lens with a mesh in the torch. Nozzles with different diameters are available for the lens. The larger the size, the better the protection.
For our purposes, No. 5 will do. This diameter allows you to get to hard-to-reach places.

Thanks to the gas lens, the electrode can be extended up to 10 mm.
When welding stainless steel with argon, you can use universal ones. The diameter depends on the thickness of the metal. For example, an electrode with a diameter of 1 mm (withstands current up to 50 A) is used for workpiece thicknesses of 0.7-1.6 mm.
Preparation of material
Just as you machine mild steel, stainless steel edges are cleaned and adjusted before welding. Clean the material with a steel brush until it shines and degrease it with any solvent.
Take into account the nuance - to shrink the seam, make the welding joint with a small gap.
Know that not everything shiny is stainless steel. You can check metal using a magnet:
- if there is no attraction, then we have stainless steel;
- if the material sticks to the magnet, then it is ordinary steel.
Thin metal connection
Welding thin stainless steel - nuances of technology. With this connection, it is recommended to place a copper plate under the workpieces.

Copper plate for comfortable connection of products
Which serves for:
- seam protection on the other side;
- heat removal;
- rigid fixation of flexible plates.
Correct device settings. stainless steel 1 mm thick is performed at 35-37 A mode and crater filling (DOWN SLOPE) for 3 seconds. Gas after welding (POST FLOW) can be set for 4 seconds - this is enough to cool the metal.
If the edges of the workpieces are well adjusted to each other and firmly fixed, then argon welding of stainless steel can be performed without filler wire.

We cook without additives
Pipe welding
We have pipelines in our everyday lives, many of which are made of stainless steel. also has its difficulties. The technology requires quality welds, which is achieved by gas protection from the inside.
How to run argon gas inside a pipe? It’s simple: one side of the pipe needs to be plugged with available materials:
- paper;
- cloth;
- rubber;
- foam rubber, etc.
Insert a gas supply tube into the plug and wrap the structure with tape or adhesive tape. The argon supply pressure is set to low (determined experimentally) so that the molten metal does not blow out. This device will help to weld pipes efficiently.
Setting up the machine for thick metal. Argon welding of stainless steel metal 3 mm thick requires a current setting of 65 A, crater filling - 3 seconds, gas after welding - 4 seconds.
Pulse Mode
In addition to the basic settings used in argon arc devices, another function has now appeared - this is Pulse. The setting allows you to weld thin and thick metal in different spatial positions. When welding stainless steel, the pulse mode reduces heat input.
To switch to this mode, you must turn on the Pulse button on the device. And with other adjustments you can set the lower and upper current limits, pulse speed (Hz) and current balance.
How to cook stainless steel correctly
At the beginning of work, do a good application of the first layer (welding the root of the seam). Once complete, tap the seam with a hammer and brush away any debris. Next, restore the anti-corrosion properties using SE etching paste. After 20 minutes, wash off the remaining paste with water. That's it, your welded joint is protected from corrosion.
In the tables below, we study and take note of different connection modes:



Tired of the text, let's watch the video:
Cooking stainless steel with foreign metal
If it is necessary to weld stainless steel with other materials (mild and low alloy steel), use a filler rod with nickel and chromium. With the following markings:
- Y310;
- Y310S;
- Y309;
- Y309L;
- Y309Mo.
These filler materials will protect against hot cracks during work.

The cost of welding stainless steel with argon across the country starts from 10-20 rubles per 1 cm. Prices differ depending on the region and the price list of companies performing such services.
Semi-automatic welding (MIG)
The protective gas environment is widely used in all industries. The process goes like this: the wire, which acts as an additive and electrode, is automatically fed into the welding zone.
The quality of the connection is affected by the correct settings: wire feed speed, gas flow and current.
So, how to cook stainless steel semi-automatically in a gas environment. There are 3 methods:
- short arc technique;
- jet transfer;
- pulse connection.

A short arc is used for thin metal plates, jet technology is used for welding thick products. The pulse technique is suitable for inexperienced welders.
Equipment and materials:
- current source with wire feeder;
- special coated wire;
- burner assembly (it’s good to have a supply of tips);
- ground terminal;
- high pressure cylinder with flow meter;
- mask and gloves.
The table shows the current settings and wire diameter based on the sheet thickness.

Before welding, bite off the excess wire (adjust the electrode extension), lower the torch to the metal, holding it with one hand, supporting it with the other, press the button.
At the beginning of welding, keep the torch close to the metal; when filling the gap with metal, move the torch away. But don't push it too far.
By changing the machine settings and practicing, you will gradually master the welding technique. Study the seam, you can even break it to look for flaws.
You are doing it wrong if:
- the edges are not melted, but hang over the metal - low speed of movement;
- the seam sticks out, does not spread to the sides - cook too quickly;
- excessive spattering - high tension.
- the composition of the gas mixture should be 70% carbon dioxide and 30% argon;
- distance from nozzle to metal 7-13 mm;
- wire extension 6-9 mm;
- Make sure the wire exit is clean;
- shielding gas consumption 6-12 cubic meters/min;
- in case of welding defects, check the ground terminal;